Conflict is as old as human
brain. Humanity has been attempting, throughout the
civilization, to solve its conflict, in a manner desirable to it. These attempts loom across a
large spectrum spanning between illegitimate methods
(absolute violent conflict like murder, genocide and war) and more refined functional procedures (persuasive conversation, dialogue,
dialectics towards mutually acceptable position like agreement, accordance and consensus).
Contemporary life in a
global village is very complex, so are the conflicts arising therein. This calls for a refined response to conflict
if we intend to build sustainable human society.
Conflict presupposes a
prevailing relationship. There can be no
conflict between parties that are not connected. Conflict actually
means estrangement in relationship; a strain or an anomaly in the conduct
of relation. Attempts to resolve
conflict is essentially to removing the strain and restoring
relationship. For that reason, response to conflict has to be one of
healing, than eliminating, to be one of inclusive, than exclusive.
This course offers a
comprehensive exploration of conflict, in three segments:
a) ‘Understanding
Conflict’,
b) ‘Cause of
Conflict’ and
c) ‘Dealing With
Conflict’.
These segments offer
understanding of what is conflict, the constituents of Conflict, forms and
factors of conflict, causes and sources of conflict and provides a four-A
methodology of handling conflict.
Segment
1. Understanding Conflict
Participants’ input: Conflict is :
Domination,
oppression, control over others, their resources, opportunities, Superiority /
inferiority complex, competition
- Prakhar
personality
aberration, impediment, restriction,
confinement - Deepa Naik;
narrow
mentality / outlook - Reza Rafat
terror,
intimidation, social discrimination, political domination Basavaraj Akki);
Elitism,
Narcissism, Rigidity - Pietro U Macleo
Stereotypes,
Prejudices - Mafugi Ceesay
Fundamentalism,
extremism, fanaticism - Alia Ruwa
Economic
hierarchy ; workers - management issues
- Abdoulie Njie ….
Conflict has as many
names as the number of forms it appears.
Contest,
Contradiction, discrepancy, controversy, incompatibility, incongruity,
inappropriateness, Difference, variation, irregularity, changeability, disparity,
deviance, inequality, disproportion, Antagonism, quarrel, duel,
hostility, enmity, feud…
Some conflicts take Physical
forms: Fight,
clash, encounter, battle, combat, violence, belligerence,
Contest, struggle, resist, race,
challenge, dispute, strike, demonstration, Morcha, picketing, bargain,
war…
Some conflict are vocal; they are called Verbal
Conflict: Heated discussion, argument, squabbling, debate, disagreement, difference of opinion,
duel that invariable take the forms of scolding, shouting, screaming, verbal
altercation.
Teasing,
Avoidance, Denial / Loss of Identity, Ignominy, Alienation, Discrimination,
racism, Casteism (Intentional and unintentional). These are Emotional Conflict.
Within an individual/group there can be inner
conflicts like: Dilemma,
quandary, catch-22, impasse, predicament, inconsistency,
incompatibility. These are called Inner
conflict, and when occur within an individual, called Intra-personal
conflicts.
Frustration,
Aggression, Aggressive Action:
arson, breaking / damaging property.
Exploitation, Discrimination, Murder, Arson, Rape,
Segregation, No hold barred Conflict. These are acts that deny the victims
their self-esteem, dignity and security.
By definition they are absolute conflicts.
II. Defining Conflict
We are social being. Society is all about
relationship. Friction is an integral
nature of relationship.
Conflict therefore is inevitable.
This conflict is defined in the following
manner.
a) When Dynamic
Differences meet, the interaction is conflict.
b) Conflict
is ‘Difference between Expected and Actual’: eg. Expected employment and actual
unemployment
c) Conflict
is Difference between Potential and Actual : gender discrimination for eg.
d) Difference
between Ideal and Actual. Value
appreciation vs. Non-adherence; belief in all being equal Vs. Treating others
as inferior or superior : gender discrimination; Constitutional gap; our
disappointment on things not being perfect….
III. Types of
Conflict
a.
Based on the Parties: Conflicts can be classified
into intra-personal conflict (within a person); interpersonal conflict (between
two individuals); group conflict (between two sets of people ; for eg., workers
and management or neighbourhood clashes); civil war (widespread national unrest
/ strife); international war (between
two nations) World wars (between two groups of countries)
b.
Based on the means of conflict: Conflict is
grouped into, ‘Physical Conflict, Verbal conflict, Emotional conflict,
Intellectual conflict, Institutional Conflict, Structural Conflict’.
Physical conflict (physical / instrument using
arms / weapons); mental / Psychological conflict (argument; debate;
logical rational strategic countering); Verbal conflict (using language:
scolding, shouting, yelling, verbal abuse…); emotional (fighting on emotional
ground: withdrawing cooperation / stop talking / ignoring…); Institutional
(fighting through established channels or institutions: police, judiciary,
grievance redressal cell; community
elders…)
c.
Based on the factors of conflict: Personality conflict (when we
do not like the general personality of a person, there is likely clash);
conflict of means; conflict of values; conflict of interest; conflict of goal…
d.
Realistic Conflict : Conflicts having definite direct cause – for
instance, ‘she insulted me; my friend ignored me; the management discriminated
some workers, when neighbouring countries provoke us, the conflict we wage is
realistic.
e.
Non-realistic conflicts are those that arise out of no
clear, direct causes. A frustrated
person fighting with every one; a drunkard fighting with people around;
ventilating frustration on unrelated parties…
f.
Functional Conflict : Those conflicts which are helpful; useful
conflicts – fight for justice, freedom, fight for truth)
g.
Dysfunctional Conflicts are those conflicts that
destroy. Conflict conducted violently
between two families end up in loss of relation, death… War for instance is
dysfunctional.
h.
Based on the Principles of conflict: Conflict is
classified as ‘Conflict of
interest, conflict of goal, conflict of values’
IV. Structure of
Conflict: Conflict has a definite structure. Based
on the nature of it conflict can be present in three structures. PLO, ABC, and GAI
a.
Structure
– I : PLO : Potential, Latent and Overt
(manifest).
Potential Conflict: The presence of inherent causes but not consciously felt. Example: A self-satisfied slave; or a self-contented traditional subjugated wife, or a healthy man not realizing the tumor in stomach, does not realize that there is conflict. However, when they come to know that they are exploited, discriminated, they begin to feel the heat.
Latent
Conflict: The presence of
conflict is consciously felt but
not articulated / expressed; tension felt by parties without expression. Example: when a suppressed community or traditional wife
realizes that they / she too have Human Rights then their present state of
life starts hurting them.
Manifest
Conflict: The expression
of conflict. Example: When the
empowered house wife articulates her grievance
openly
Satyagraha
proposes that a conflict has to be
addressed at its potential stage or latent stage. Response to conflict after it has begun to
manifest is ( too late) the same as fire fighting. We can do only damage reduction. That’s a
curative process. Satyagraha gives
priority on preventive process. A stitch
in time saves nine.
b.
Structure – II: ABC: Conflict Triangle-ABC
Conflict Behavior
Conflict Context:
Every conflict is determined by
the party’s attitude, behavior and the situation / Context s/he lives.
c.
Conflict Structure- III:
GAI: Goal Actor Impediment.
The impediment (obstruction / hindrance)
to the pursuit of Actor is called a Frustration. The Actor’s extra effort to remove the
obstruction from the path to his/goal is called Aggression. Aggression can be physical, mental, emotional,
Psychological or all combined in varied degrees.
I.
Factors of
conflict
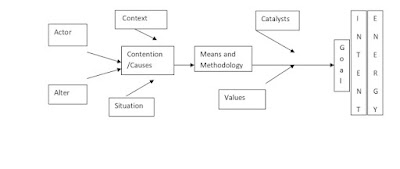
There are Twelve factors that together constitute a conflict. They are: Actor, Alter, Issue, Means, Methodology, Goal, Intention(Purpose), Situation, Context, Values, Catalysts and Energy that govern…
Catalysts: Qualities such as : Prejudice,
stereotype, anger, hatred, enmity, selfishness, impoliteness, distrust are some
of the catalysts, that augment any conflict that come on the way.
Prepared and shared By:
D John
Chelladurai, Prof. and Head, Dept of
Gandhian Studies, MGM University; djohnchelladurai@gmail.com ;
hod.gandhianstudies@mgmu.ac.in ; +91 - 94 219 25 146 (whatsapp)







So much educative and interesting,I really learned a lot and it makes me understand a lot in conflict
ReplyDelete